In the quest for optimal health, certain nutrients play a crucial role, and none are more deserving of the spotlight than calcium and vitamin D. These powerhouse nutrients work in harmony to support various bodily functions and promote overall well-being. In this blog, we will explore the benefits of calcium and vitamin D for health, daily requirements, top food sources, risks of deficiency, their relationship with other nutrients, and practical strategies to ensure you’re meeting your calcium and vitamin D needs.
The Benefits of Calcium and Vitamin D for Health
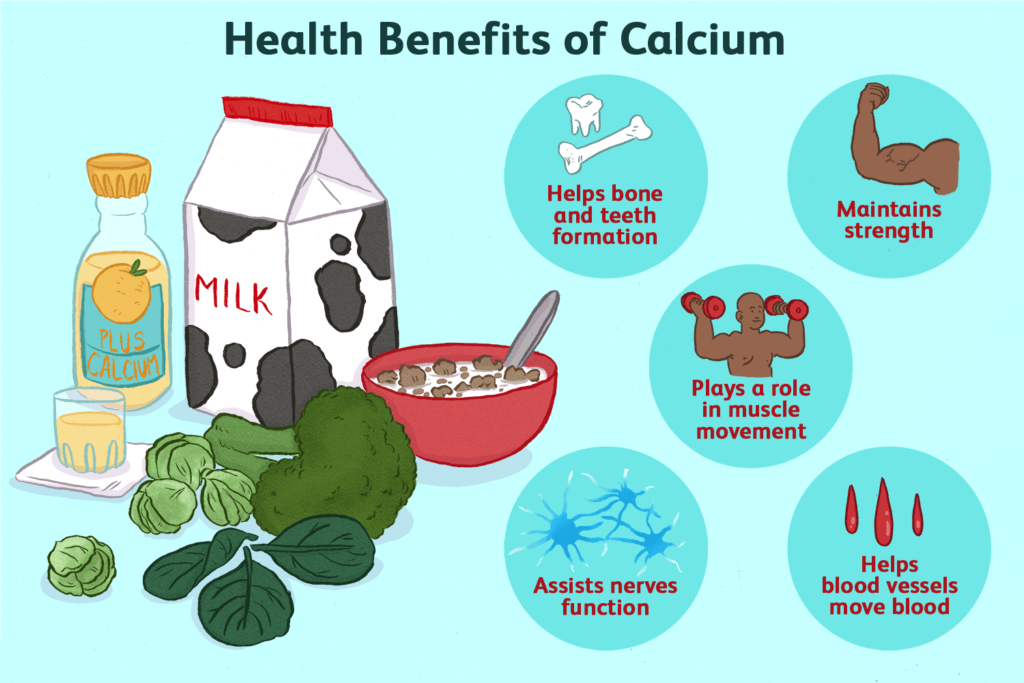
Calcium and vitamin D offer an array of health benefits that extend beyond strong bones. Calcium is vital for supporting nerve transmission, regulating blood pressure, and ensuring blood clotting functions effectively. On the other hand, vitamin D plays a crucial role in calcium absorption, reducing inflammation, and promoting healthy cell growth. Here are some other health benefits of calcium & vitamin D:
- Bone health: Calcium is the main building block of bones, and vitamin D helps the body absorb calcium. Adequate intake of calcium and vitamin D can help to prevent osteoporosis, a condition that causes bones to become weak and brittle.
- Muscle function: Calcium is also important for muscle function. It helps to keep muscles contracting and relaxing properly.
- Immune system support: Vitamin D plays an important role in the immune system. It helps the body fight off infection and disease.
- Other health benefits: Calcium and vitamin D may also be beneficial for other health conditions, such as high blood pressure, heart disease, and cancer.
How much calcium and vitamin D do I need each day?
The recommended daily intake (RDI) of calcium for adults is 1,000 milligrams (mg). The RDI for vitamin D is 600 international units (IU) for adults under age 70 and 800 IU for adults over age 70.

Top Sources of Calcium and Vitamin D
While supplements can bridge nutrient gaps, it’s always preferable to obtain calcium and vitamin D from natural food sources. Explore a diverse range of dairy and non-dairy options that offer high calcium content, including milk, yogurt, cheese, leafy greens, and fortified plant-based milk alternatives. Discover the best sources of vitamin D, such as fatty fish (salmon, mackerel), egg yolks, fortified cereals, and safe sun exposure.

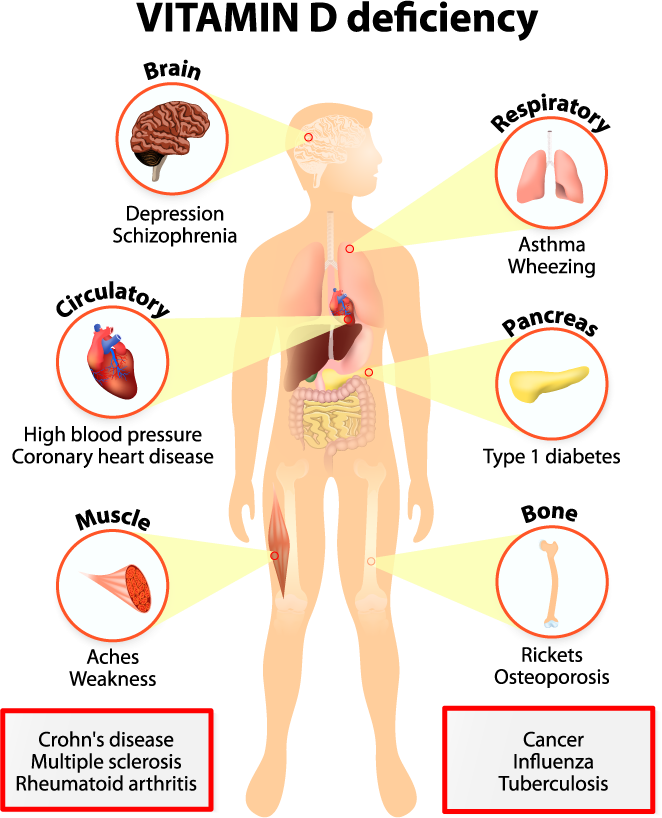
What are the risks of calcium and vitamin D deficiency?
- Osteoporosis: Calcium and vitamin D deficiency can lead to osteoporosis, a condition that causes bones to become weak and brittle. Osteoporosis can increase the risk of fractures, especially in the spine, hip, and wrist.
- Muscle weakness: Calcium and vitamin D deficiency can also lead to muscle weakness. This can make it difficult to perform everyday activities, such as walking, climbing stairs, and lifting objects.
- Increased risk of infection: Vitamin D deficiency can increase the risk of infection. This is because vitamin D plays an important role in the immune system..
Ensuring Adequate Calcium and Vitamin D Intake
Achieving optimal levels of calcium and vitamin D is attainable with a mindful approach. Incorporating calcium-rich foods into your daily meals, getting safe sun exposure for natural vitamin D synthesis, and considering supplementation if necessary are effective strategies to ensure you meet your nutritional needs.
In addition to getting enough calcium and vitamin D from food or sup
Conclusion
Calcium and vitamin D form a powerful duo that contributes significantly to our health and well-being. From supporting bone health to bolstering our immune system and beyond, their benefits are extensive. By understanding the recommended daily intake, exploring diverse food sources, and taking a holistic approach to nutrition, you can harness the full potential of calcium and vitamin D to optimise your health and vitality.
